measuring graphene thickness|graphene layer thickness : importer It is established that the graphene-substrate adsorbate layer and imaging force, in particular the pressure the tip exerts on the surface, are crucial components in the accurate measurement of graphene using AFM. Graphene has emerged as a material with a vast variety of applications. The electronic, optical and mechanical properties of graphene are strongly influenced by the . WEBBARPRO, Criada em 2005 é uma empresa especializada em utensilios de bar para uso profissional, para atender Barman e Bartender mais exigentes. Sempre atendendo Revendas, com um portifolio do mais requisitado. BARPRO, Importadora e distribuidora de utensílios de bar. Para uso de Barman e Bartenders.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da AMC
We provide two easy-to-use methods to determine the number of graphene layers based on contrast spectra: a graphic method and an .It is established that the graphene-substrate adsorbate layer and imaging force, in particular the pressure the tip exerts on the surface, are crucial components in the accurate measurement of graphene using AFM. Graphene has emerged as a material with a vast variety of applications. The electronic, optical and mechanical properties of graphene are strongly influenced by the .Topographical approaches to measuring graphene thickness September 28 2012 An EFM phase image showing one layer graphene (1LG) and the interface layer Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) in the tapping (intermittent contact) mode is a commonly used tool to measure the thickness of graphene and few layer graphene (FLG) flakes on silicon oxide surfaces. It is a convenient tool to quickly determine the thickness of individual FLG films. However, reports from literature show a large variation of the .
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a commonly used technique for graphene thickness measurement. However, due to surface roughness caused by graphene itself and variation introduced in AFM . In Fig. 2, the thickness of SiO 2 is varied while the thickness of the graphene layer is fixed at 3.4 Å. As the thickness of the SiO 2 layer increases, the number of Kiessig fringes increases as shown in Fig. 2a. In order to fully express the dense and narrow fringes, more data points are required, which implies that, in actual experiments, the measuring time is . Therefore, accurately measuring the thickness of graphene is crucial for understanding its properties and potential uses. What is the theoretical thickness of graphene? Theoretical calculations predict that graphene has a thickness of 0.335 nanometers, which is equivalent to the length of one carbon-carbon bond. Microfabrication of graphene devices used in many experimental studies currently relies on the fact that graphene crystallites can be visualized using optical microscopy if prepared on top of .
The standard deviation of the single measurement of the measured reflectivity of single-layer, two-layer, five-layer, eight-layer, and ten-layer graphene films increases with the number of graphene film layers, because the multilayer graphene films are prone to interlayer folds and thickness non-uniformity during the transfer process, which . Conventional methods to measure thermal properties of bulk materials or thin film with microscale thickness have been applied to measure thermal properties of graphene and produced meaningful results on thermal properties of graphene [15,16,17].However, these conventional methods usually entail very complicated procedures for the sample preparation . However, due to surface roughness caused by graphene itself and variation introduced in AFM measurement, graphene thickness is difficult to be accurately determined by AFM. In this paper, a histogram method was used for reliable measurements of graphene thickness using AFM. The influences of various measurement parameters in AFM analysis .
The thermal conductivity (κ) in graphene is measured by a simple and portable F–P resonator.The transient measured κ in graphene decreases with increasing air pressure.. The impact of convective heat transfer on κ transient measurement is verified by COMSOL simulation.. The predicted κ at 0 Pa of 10–layer graphene is determined to be 194.48 W/(mcommonly used tool to measure the thickness of graphene and few layer graphene (FLG) flakes on silicon oxide surfaces. It is a convenient tool to quickly determine the thickness of individual FLG films. However, reports from literature show a large variation of the measured thickness of graphene layers. This paper is focused on the imaging . Ellipsometry mapping was also applied for measuring the thickness of the graphene layer produced by sublimation epitaxy on silicon carbide [2]. The signal measured by ellipsometry depends on the thickness and the optical constants of the layer and thus, the thickness cannot be directly determined.
Si/SiO2/Graphene multilayer system varies with the thickness of SiO2 and graphene [3], [4]. While the former is rather triv-ial, the latter provides the physical foundation for identifying the thickness of the graphene layer, and thereby the number of layers, solely based on measuring the reflectivity of theassist in characterization of the graphene refractive index. As the name implies, the key to this technique is to measure multiple samples, varying the thickness of the graphene or the substrate in which it is deposited while ensuring that the varied conditions don’t lead to variation in graphene properties. A mono-layer to bi-layer ˝ ˚ ˇ Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a commonly used technique for graphene thickness measurement. However, due to surface roughness caused by graphene itself and variation introduced in AFM measurement, graphene thickness is difficult to be accurately determined by AFM. In this paper, a histogram method was used for reliable measurements of .Graphene (/ ˈ ɡ r æ f iː n /) [1] is a carbon allotrope consisting of a single layer of atoms arranged in a honeycomb planar nanostructure. [2] [3] The name "graphene" is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, indicating the .
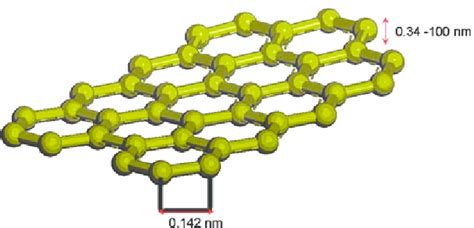
thickness of single layer graphene
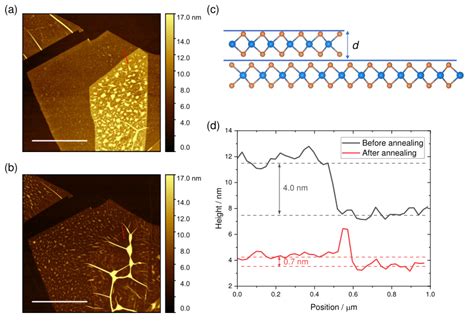
But it is usually slow and may damage the surface of graphene during the measurement. In addition, the measurement offset (∼ 0.7 nm) of AFM equipment is usually larger than the thickness of single layer graphene , thus introduces large inaccuracy. Unconventional quantum Hall effect has also been applied to differentiate monolayer and . The graphene thickness can be determined straightforwardly with LEEM from the reflectivity of the low-energy . Figure 1: LEEM, STM and macroscale potential measurement of graphene on SiC. Using a nominal thickness of graphene of 0.335 nm 5, a three-dimensional (3D) Young’s modulus of the free-standing graphene sample can be calculated as E 3D = ~920 GPa in the uniaxial stress . Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) in the tapping (intermittent contact) mode is a commonly used tool to measure the thickness of graphene and few layer graphene (FLG) flakes on silicon oxide surfaces. It is a convenient tool to quickly determine the thickness of individual FLG films. However, reports from literature show a large variation of the measured .
The graphene layers were prepared on the Si-terminated face of 0 0 0 1 oriented 6H-SiC single crystal wafer of 2 in. size by high temperature sublimation process [7] developed at Linköping University.While growth on 6 × 12 mm 2 area resulted in one monolayer (1ML) graphene as demonstrated in [7], the same growth conditions did not sustain the same .
Simultaneous measurement of the refractive index and thickness of graphene oxide/gold multilayered structure for potential in dopamine sensing using surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy . enhancement of the modified chip towards DA and highlighted the technique's appropriate and sufficient potential to measure thickness and refractive index .
Graphene has emerged as a material with a vast variety of applications. The electronic, optical and mechanical properties of graphene are strongly influenced by the number of layers present in a sample. As a result, the dimensional characterization of graphene films is crucial, especially with the continued development of new synthesis methods and applications. A number of . Although these methods require fitting and further analysis of the spectrum to extract the number of graphene layers, AFM can directly measure the thickness and damage in graphene 80, 83 . From .
Measuring the thickness of few-layer graphene by laser scanning microscopy. In G. Jones, T. Lipe, R. P. Landim, & A. Koffman (Eds.), Conference on Precision Electromagnetic Measurements (pp. 456 - 457). IEEE, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. Optical microscopy and Raman spectroscopy images of the CVD-grown graphene. The optical images (first column) and various Raman mapping images of the integrated intensities of the Si- (450–600 .

linux stress test hard drive

thickness of monolayer graphene
Resultado da FuteMAX – FUTEBOL – UFC – ESPORTES E MUITO MAIS, SEM ANÚNCIOS! Futmax é a plataforma perfeita para assistir futebol ao vivo de qualidade, livre dos incômodos dos sites cheios de anúncios irritantes.
measuring graphene thickness|graphene layer thickness